Causes of violations of the outflow of bile from the gallbladder. Gallbladder and its diseases
Pain in the gallbladder is an important signal of the body, which indicates a violation of work in this organ. They occur for various reasons, which often complicates their diagnosis. Often, problems with the gallbladder appear on the background of the usual overeating or severe psycho-emotional disorder. In other cases, the appearance of pain in the gallbladder becomes a consequence of serious pathologies.
Common signs of diseases of the gallbladder and ducts
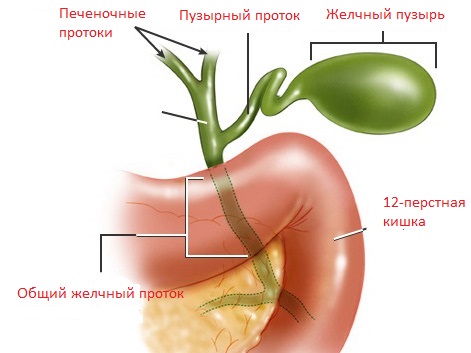
Liver cells produce bile, which is passed through the bile capillaries into the hepatic duct. From it, it is partially transported into the gallbladder, and the rest - into the duodenum. In the gallbladder, the fluid is concentrated, and when food enters the duodenum, concentrated bile is released. Fatty foods and egg yolks most actively induce its elimination.
For a person, the normal composition of bile and its timely elimination are very relevant. It promotes the digestion and absorption of fat by the body, including fat-soluble vitamins. Bile acids invigorate the intestines and remove hazardous substances from the body: for example, heavy metal salts, toxins, decomposition products of drugs. Bile also contains bilirubin, a coloring pigment.
Diseases of the gallbladder accompany such common symptoms, as:
- pain in the gallbladder;
- dyspeptic disorders: nausea, belching, vomiting;
- yellowness of the skin;
- pruritus
Where exactly does the gallbladder hurt? The pain syndrome is usually localized in the right hypochondrium, less frequently in the epigastric zone. The pain can be given to the right shoulder or shoulder blade, some patients have headache with gallbladder diseases. Palpation of the abdomen in the right hypochondrium may show pronounced pain. Belching is accompanied by a bitter taste. Nausea and vomiting are companions of biliary colic. Jaundice is associated with temporary or permanent blocking of the bile duct or hepatic duct, in this case it is called mechanical.
Types of diseases of the gallbladder and ducts
Diseases of the gallbladder are pathological conditions, which are based on a violation of the body’s ability to remove the bile necessary for digestion in a normal volume. Causes of pain in the gallbladder are usually associated with blockage and pain in the bile ducts, inflammation and tumors.
Experts identify the following groups of diseases that occur with the development of dysfunctional disorders of the biliary tract and gallbladder:
- Dyskinesia of the biliary tract. This disease occurs against the background of a violation of the contractile activity of the tissues of the gallbladder and its ducts. As a result, the removal of fluid from the body is difficult. Unhealthy food, diseases of the digestive organs, hormonal imbalances, food allergies, chronic stress, age-related changes can lead to this disease. A complication of biliary tract dyskinesia is cholelithiasis.
- Chronic cholecystitis. This is an inflammation of the gallbladder, often occurring against the background of intestinal infections, and giardiasis. When cholecystitis qualitatively changes the composition of bile, there is a violation of its outflow, the formation of stones.
- Acute cholecystitis. This is an extremely painful inflammation of the gallbladder caused by blockage of the bile ducts. It is often the result of gallstone disease.
- Cholelithiasis. This is an inflammation of the gallbladder, against the background of which concrements form in the organ itself or its ducts. Predisposing factors are elevated cholesterol in the blood, genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance,.
- Postcholecystectomy syndrome. This pathology occurs after resection of the gallbladder. The development of the disease can contribute to the stones, remaining in the bile ducts, the narrowness of the duct itself at the place of confluence with the duodenum, inflammation of the small intestine and duodenum.
- Benign and malignant pathologies of the gallbladder (polyps, oncology). These are serious neoplasms in the gallbladder that must be surgically removed. They appear as a result of gallstone disease and the age characteristics of the patient.
Symptoms
Every disease of the gallbladder, a symptom of which is pain, has its own signs and symptoms.
Symptoms of dyskinesia:
- pains of cramping and whining character in the right hypochondrium;
- chronic fatigue;
- sleep disturbance and appetite;
- deterioration of sexual functions;
- apathy, depression.
Symptoms of chronic cholecystitis:
- recurrent hepatic colic;
- pains in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the right shoulder and shoulder blade;
- nausea, vomiting.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis:
- pronounced pain syndrome;
- jaundice sometimes develops.
Symptoms of gallstone disease:
- acute attacks of biliary and hepatic colic;
- pain;
- nausea, vomiting;
- stool discoloration;
- dark urine;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- fever
Symptoms of postcholecystectomy syndrome:
- surrounding pains in the right and left hypochondrium, as well as in the epigastric part;
- nausea, vomiting;
- gas formation;
- problems with the chair.
Symptoms of benign and malignant tumors:
- signs of chronic cholecystitis;
- drastic weight loss;
- jaundice;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathologies of the gallbladder is complicated by the fact that at the initial stage they are rarely detected, since the symptoms of gallbladder diseases usually resemble signs of other diseases: for example, digestive disorders, diseases of the digestive tract organs and much more.
Ultrasonography can help diagnose the appearance of malignant and benign neoplasms, and diagnose signs of gallbladder disease (dyskinesia and gallstone disease).
However, the following diagnostic tests will help to more accurately confirm the symptoms of gallbladder disease in women and men:
- laboratory diagnostics: biochemical blood test;
- duodenal intubation, which is carried out with the aim of obtaining biological fluid from the gallbladder - bile, to study its chemical composition;
- secondary ultrasound diagnostics;
- cholecystography.
Ultrasound is not limited to the stage of diagnosis. In addition, it can be administered in the process of medical therapy and during the rehabilitation process, the task of which is to detect complications and the appearance of tumors.
Treatment
Treatment of pain in the gall bladder is the appointment of drug treatment with additional ultrasound monitoring of the state of the abdominal organs. How to remove pain in the gallbladder?
Drug therapy is complex and includes the following techniques:
- the appointment of antispasmodic, antimicrobial, choleretic and anthelmintic drugs and plant-based fees;
- strict fractional diet with the obligatory use of mineral waters;
- washing the bile ducts (tubage) with the help of salts, sorbitol and magnesia;
- physiotherapeutic effect: laser and acupuncture.
Gallstone disease is treated by chemical and ultrasonic grinding and dissolution of stones in the gallbladder. These sparing non-surgical methods are applied only if the disease is not running, and the size of the stones is not more than 20 mm. Otherwise, an operation is performed, as a result of which the gallbladder is removed in full.
Prevention
Prevention of gallbladder disease is the restoration of the physiological function of the gallbladder and its ducts and the stabilization of the bile excretion process. Even after resection of the gallbladder with the help of appropriate prevention, it is possible to normalize the full-fledged synthesis of bile by the liver cells.
Preventive work includes the following areas:
- patient compliance with a specific menu in case of gallbladder disease in the form of an individually selected diet, depending on the nature of the disease (and the diet must be strictly followed for one year);
- refusal of addictions, such as alcohol and nicotine, abuse of fried, smoked, salty and fatty;
- exclusion of serious physical activity;
- regular physical therapy;
- phytotherapy with special herbal preparations and herbs on the recommendation of the attending physician;
- preventive use of mineral waters;
- rest in resorts - sources of mineral waters.
Any prophylaxis is carried out with the direct participation of the attending physician with concomitant ultrasound diagnostics to monitor changes in the status of the organs of the digestive tract. If you follow the above rules, you can forget about where the gall bladder is and how it hurts.
What can and can not be eaten in diseases of the gallbladder?
What to do if the gallbladder is constantly sore? Of course, pay attention to your diet - any doctor will answer. Healthy food, a balanced diet - these are the first criteria on the path to recovery and restoration of the functional activity of the entire digestive tract.
The first thing you need to pay attention to is how many times a person takes food per day. It is advisable to adjust your diet for 6, and preferably 7 meals a day. In this case, the approximate interval between the previous and the next meal will be no more than two and a half hours. But as a result, bile will not have a chance to stagnate in the walls of the gallbladder, which contributes to normal digestion and the health of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
What can you eat with gallbladder disease? It is allowed to use unsweetened tea, decoctions based on vegetables, juices diluted with water, dried fruit compotes, jelly. In moderation, you can eat cereals, lean meats and fish, boiled eggs, vegetable oils, preferring olive, rye bread.

What can not be a disease of the gallbladder? From the daily diet will have to completely remove the harmful food - salinity, smoked, spicy and fatty, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, raw fruits and vegetables, products with essential oils (radishes, garlic, onions, etc.).
If we sum up the above, it should be noted that today there are a lot of causes and predisposing factors that negatively affect the functional activity of the organs of the digestive tract. Fatty foods, food on the go, sedentary lifestyle, stress, and an irregular rhythm of life lead to digestive disorders, but most people do not pay attention to it. As a result, they enter the doctor’s office after the gallbladder starts to hurt.
The clinical picture and treatment of the gallbladder are closely related to the causes of the development of pathologies and the age of the person. Unfortunately, it is impossible to solve all the problems with the help of modern medicine, especially with the development of an irreversible pathological process; therefore, it is undesirable to delay treatment with the occurrence of gallbladder pain. Any disease is best treated on time and without health consequences.
Useful video about cholecystitis
The dynamics of modern life, with its stresses, snacking on the go and the absence of a culture of healthy eating, led to gallbladder diseases being among the most common diseases.
The removal of this body has become a common and relatively uncomplicated operation. In surgical clinics, it is performed according to the smallest medical indications. In view of what a false impression about the insignificant value of the gallbladder for the functioning of the body. This statement is incorrect. Hippocrates wrote about its irreplaceable value for the life of the organism as a whole. So what is the gallbladder?
Concept and functions
 - This is one of the organs of the digestive system. It is located at the surface of the liver on the right side, below. Connects to the liver through bile duct. The body accumulates bile, which in the process of digestion flows from it into the duodenum.
- This is one of the organs of the digestive system. It is located at the surface of the liver on the right side, below. Connects to the liver through bile duct. The body accumulates bile, which in the process of digestion flows from it into the duodenum.
The human gallbladder (a healthy organ) has a length of about 8 cm, and a volume of up to 60 mm3.
Liver cells produce a thick, dark and very bitter fluid called bile. Through the capillaries and hepatic bile ducts, this digestive juice is sent to the bile storage tank, from where it is consumed as needed. Bile production occurs constantly, but its participation is required only in the process of digestion.
So what is the gallbladder for? Its main function is to collect, store and dispense bile into the intestine. When entering the intestine of bile, such processes occur as:
- change of gastric digestion to intestinal;
- neutralization of the destructive effects of gastric juice on the intestinal wall at the time of receipt of food from the stomach;
- improving overall intestinal motility;
- increased absorption of vitamins A, E, K, and D;
- blocking development in the intestines and appendix of pathogenic bacterial flora.
Bile accumulating organ is directly involved in the excretory system of the body. Some substances (metals, steroids, etc.) are not filtered by the kidneys, and therefore are eliminated from the body through bile through excretion.
Like all internal organs, the body's biliary system tends to wear out. What are the diseases of the gallbladder, their manifestations, what are treated and what are the consequences?
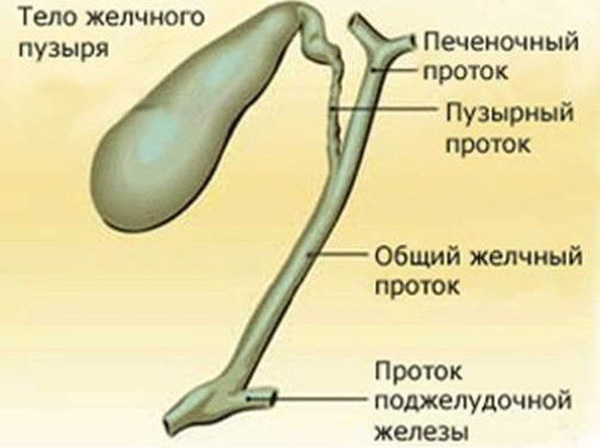
The structure of the gallbladder
There are several types of dysfunction of the biliary system. The disease occurs due to malnutrition, poor water, dehydration.
Common diseases of the biliary system:
- gallstone disease (ICD);
- dyskinesia.
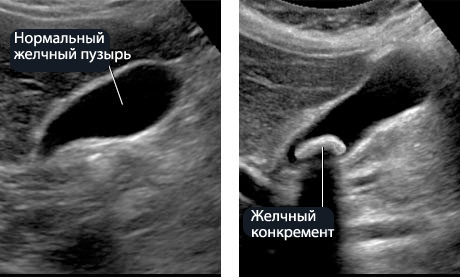
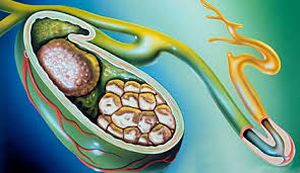 Gallstone disease (ICD) is the formation of sand and calculi in the biliary tract. Stagnation of bile or a change in its composition leads to stone formation. The process of gallstone disease is long and almost asymptomatic. Learn about the formation of calculus can be random, when examined by a doctor.
Gallstone disease (ICD) is the formation of sand and calculi in the biliary tract. Stagnation of bile or a change in its composition leads to stone formation. The process of gallstone disease is long and almost asymptomatic. Learn about the formation of calculus can be random, when examined by a doctor.
The disease makes itself felt in the movement of stones, which can provoke food, awkward movement, a blow, etc.
Symptoms of gallbladder and liver diseases are as follows:
- sharp girdle pains in the lumbar back;
- epigastric tenderness;
- nausea;
- vomiting
- chills.
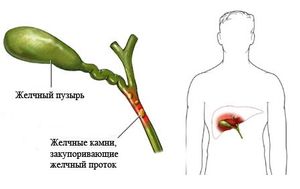 Cholecystitis occurs against the background of an imbalance of the common bile choke and is divided into acute and chronic. Acute form of the disease - blockage of bile ducts due to the formation of stones. Usually stones are formed in the cystic body, but they can also block the bile ducts.
Cholecystitis occurs against the background of an imbalance of the common bile choke and is divided into acute and chronic. Acute form of the disease - blockage of bile ducts due to the formation of stones. Usually stones are formed in the cystic body, but they can also block the bile ducts.
Stones up to 3 mm in size are able to exit independently through the bile ducts. Larger stones block the bed, causing colic and pain. This situation requires urgent surgical intervention.
Signs of acute cholecystitis:
- sharp paroxysmal pain under the ribs;
- throbbing pains in the right side of the body;
- temperature;
- yellowing of the skin.
Chronic cholecystitis can develop without the formation of stones. Causes of bile duct:
This form of liver and gallbladder disease has the following symptoms:
- background pain in the upper quadrant on the right;
- nausea;
- belching.
 Dyskinesia occurs in violation of the motility of the digestive organs. The disease is characterized by a deterioration of the tone of the walls and valves of the bile ducts, which leads to a violation of bile flow. Types of dyskinesia:
Dyskinesia occurs in violation of the motility of the digestive organs. The disease is characterized by a deterioration of the tone of the walls and valves of the bile ducts, which leads to a violation of bile flow. Types of dyskinesia:
- hypertensive (increased tone);
- hypotonic (reduced tone).
Hypomotor dyskinesia - bile stasis in the bile ducts. Distinctive symptoms of the disease:
- general lethargy;
- lack of appetite;
- background gnosis in the right side of the body.
Hypermotor option - the accelerated separation of bile. In patients with dyskinesia, there is constant irritability, a decrease in vital activity, a failure of the hormonal background.
Symptoms of biliary disease
Indirect signs of liver disease and bile accumulation, symptoms:
- dryness or bitterness in the mouth, taste of iron;
- skin pigmentation, skin inflammatory reactions;
- recurrent gastrointestinal disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- intermittent pain in the abdomen and lower back, in the pancreas area.
Obvious signs of illness are characterized by symptoms such as:
- acute girdling pain in the lumbar and right hypochondrium, accompanied by nausea (the most severe pains with such symptoms are observed when the bile ducts are blocked and when stones and sand come out);
- indigestion, accompanied by nausea, diarrhea;
- very dark foam urine;
- obstructive jaundice.
Pain and signs of disorders in the biliary system
 Dysfunctional changes in the biliary system of the body manifest themselves as a constant whining and pulling background in the right hypochondrium.
Dysfunctional changes in the biliary system of the body manifest themselves as a constant whining and pulling background in the right hypochondrium.
The disease of the biliary system is characterized by constant pain in the lumbar region, along the spinal column and under the scapulae. Because of this, patients often sin on kidney disease or back problems.
In the initial stages of the disease, the symptoms manifest themselves with short-lived paroxysmal pain spasms. Gall bladder problems begin after eating, especially if the food is fatty, spicy, smoked. These are not yet acute and extremely painful attacks of an already developed pathology, but quite tolerable, not very pronounced, dull.
Any disease of the biliary system is always accompanied by nausea and bitterness in the mouth, empty belching, unpleasant sensations in the right side of the body - from the subclavian area to the pelvis.
Pain in the gallbladder can occur or worsen when coughing, with a sudden change in body position, respiratory failure.
Disconnected gallbladder
 The conditional name “disabled gallbladder” is unofficially used by ultrasound operators to designate an atrophied organ. The loss of the body of its working qualities occurs in the absence of treatment, if the patient's liver and gallbladder disease is ignored.
The conditional name “disabled gallbladder” is unofficially used by ultrasound operators to designate an atrophied organ. The loss of the body of its working qualities occurs in the absence of treatment, if the patient's liver and gallbladder disease is ignored.
When the bile system becomes clogged with sand and stones, the organ is unable to contract and gradually atrophies.
In the non-functioning gallbladder, accumulation of pus can begin, and this is the path to sepsis and even peritonitis.
A variant of sclerosis - shrunken gall: an atrophied organ dries to the liver with a clot of dead tissue. Also known is the transformation with the deposition of calcium salts, as a result of which the walls of the organ harden and calcify.
Kink in body
What is a gallbladder? Organ digestive system, biliary tract. It has an elongated pear shape and consists of:
- bottom (the widest part protruding beyond the edge of the liver);
- body (tapering middle section);
- cervix (the narrowest part of the organ from which the cystic duct extends).
Kink (bend or torsion) - is a modification of the shape of the body. Causes:
- concretions overflow;
- flick;
- binge eating;
- sedentary lifestyle.
A congenital form of inflection is an underdevelopment of an organ in the womb. In this form, the bladder is located remotely from the liver, and therefore excessively mobile.
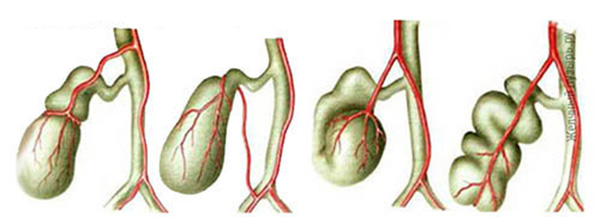
Types of inflection of the gallbladder
The resulting state of organ deformity is diagnosed only with ultrasound, especially if the bend is small. At the initial stage of the disease, the deformed gallbladder does not declare itself. Problems are identified with irreversible changes. In case of significant damage, the symptoms are similar to the general symptoms of the disease of the biliary organs:
- nausea;
- pain in hypochondrium and lower back;
- problems with the chair;
- bitterness and dry mouth;
- lack of appetite.
The deformation of the bladder is threatened by the stagnation of bile, the development of cholecystitis, and the formation of stones. With a neglected form of the disease, there is a high probability of necrosis or perforation of the wall of the organ and the outpouring of its contents into the abdominal cavity. Peritonitis develops. In such a situation, emergency surgical intervention is vital.
Useful video
In the following video you can find out more information about gallbladder diseases:
Conclusion
- The gallbladder is an important link in the body's digestive and excretory systems.
- Painful attacks in the hypochondrium and lower back, indigestion and bowel movements, bitter heartburn and dry mouth are all manifestations of a liver disease and an adjacent organ that accumulates bile.
- In the absence of due attention to the manifestations of the disease, inflammation or atrophy of the organ occurs, stones appear, which is fraught with cholecystectomy.
The gallbladder is an organ in digestive system a person who serves to accumulate bile, with subsequent release into the small intestine to facilitate the digestion of fat.
Gallbladder disease is quite common. Among other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is in 3rd place. Most often this disease occurs in people over 50 and mostly in women.
Where is the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is located in the right side of the abdominal cavity, under the liver, near the duodenum, in form resembles an oval pouch or pear, about the size of a chicken egg.
The gallbladder does not belong to vital organs and in the case of gallbladder disease, it can be surgically removed, but the full value of the functioning of the body will change.
The main causes and mechanisms of disease development
 All causes of gallbladder disease can be classified into separate groups:
All causes of gallbladder disease can be classified into separate groups:
- infection, getting into the gallbladder, forms inflammation of its mucous membrane, which further leads to cholecystitis. This may be intestinal or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Proteus;
- changes in the chemical composition of bile or in the ratio of direct components (cholesterol, protein, acids, minerals) indicate that a stone appeared in the resulting lumen, and the first stage of gallstone disease began, or cholesterosis develops when cholesterol accumulates on the gallbladder walls;
- disruption of the supply of gallbladder tissues with nerves has a detrimental effect on the contraction of its walls, which will further cause the development of dyskinesia of the gallbladder and destabilization of work in general (bile does not enter the small intestine at the appropriate time and not completely);
- inflection of the gallbladder can be genetically inherited from parents;
- deformation of the genome structure of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder leads to the development of a benign and malignant tumor.
Symptoms of gallbladder disease
There are several types of gallbladder disease. The symptoms of each of them have different manifestations and nature.
Regardless of the cause of the disease of the gallbladder or biliary tract, the patient is accompanied by a number of symptoms and in how the gallbladder hurts a person has several features:
- The pain is concentrated mainly on the right side under the ribs. With polyps, it is absent, but with cholecystitis and stones - pronounced. After eating, especially fried and greasy, during the day, the pain increases. Due to the release of stone from the gallbladder, a blockage of the bile duct occurs, which causes a sharp stabbing pain (hepatic colic).
- Digestive disorders occur due to the innervation of the gallbladder. Periodically, nausea, vomiting, bloating and problems with the stool.
- An unpleasant bitter aftertaste and crimson color of the tongue is a mandatory sign of a problem with the gallbladder and liver.
- The saturated color of urine is another cause for concern about the state of the gallbladder.
- Bright feces indicates a lack of bile in the intestine.
- Jaundice is a noticeable sign that the gallbladder is disturbed and bile enters the bloodstream, where it is deposited on the tissues of the body.
These symptoms do not always occur at the same time. Their combinations depend on the specific disease.
Diagnosis of gall bladder problems
Symptom detection is only the first step to determining a disease. In order to clarify the problem, to prescribe the correct treatment, additional diagnosis is necessary.
- a clinical blood test will very accurately reveal the inflammation, as in this case, the results will show an increase in the number of leukocytes and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- duodenal intubation is a study of bile, using a special flexible tube (probe), which is placed by patient through the mouth into the duodenum, where it collects the necessary material for examination.
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs makes it possible to identify abnormalities, stones and polyps in the gallbladder.
- fine needle biopsy is a method of examination, which introduces a special needle, which captures the necessary tissue for subsequent analysis, in order to exclude a tumor.
- x-ray contrast study - a contrast agent is injected intravenously, so that during congestion in the gallbladder it can be examined, to determine the size and shape.
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging more advanced methods to detect even the smallest formations in the gallbladder, which allows you to instantly respond to the problem and quickly eliminate it.
Treatment of gallbladder diseases
In order for the treatment to be successful, complex therapy is necessary. However, there are several factors that will favorably affect the well-being of the gallbladder:
For any gallbladder disease, medication is prescribed by a doctor based on diagnostics and test results.
The most common diseases affecting the gallbladder, symptoms and basic facts about them:
Folk remedies
The most common gallbladder diseases are treated with folk remedies, but only for the beginning it is necessary to make a thorough diagnosis with specialists.
It is best to resort to plant components, allowing to destroy the calculus, to subsequently withdraw it.
You can take the St. John's wort (he is holed) pour water and boil for several minutes on a small hob. Half a liter requires 2 tablespoons of herbs. Broth is filtered and drunk at 50 mg before meals.
 Strawberry tea will be delicious and extremely useful. It is necessary to pick 2 strawberry bushes with berries and tendrils on the teapot with boiling water to steam them.
Strawberry tea will be delicious and extremely useful. It is necessary to pick 2 strawberry bushes with berries and tendrils on the teapot with boiling water to steam them.
Cholesterol stagnation leads to stone formation in the gallbladder, therefore it is impossible to prevent its excess in the body and use choleretic agents. These include vegetable juices, but only in a certain mix and in appropriate proportions. You will need beets, carrots and cucumber. Of these, you need to get the juice, where from the first component - 40 ml, and from the other two - 80 ml, mix everything. Start drinking in the mornings and evenings with one teaspoon, gradually increasing the dosage to half a glass at a time.
Dissolve bile can spoon natural olive oil, drunk before dinner. For three days, you can achieve a great effect.
Fully clear the gallbladder for 5 weeks can fresh black radish juice, drunk on an empty stomach.
To improve the gallbladder, it is not bad to take 2 yolks from homemade eggs one hour before breakfast, and after and before lunch for 14 days.
A little bit about the structure and function of the gallbladder
The gallbladder is of great importance for the human body. It is this organ that accumulates bile, which the liver produces. To date, no one is surprised. When the work of this body is disturbed, digestive disorders are observed. Symptoms of various gall diseases have their differences, but most often they are similar. For this reason, it is important to find out in time what could have provoked inflammation.
Symptoms of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis
Often the doctor during the examination finds stones in the bile ducts or in the bladder. Most predisposed to the disease are people who are overweight, impaired metabolism. It is worth noting, it may not be known at all for a few years about yourself, then during the examination the doctor discovers pathology. Hepatic colic may occur due to stones. She has quite unpleasant signs:
- Acute pain after drinking alcohol, as well as after exercise, eating fatty, fried foods.
- Unpleasant sensations are localized under the right edge, sometimes given to the chest, aggravated by movement, deep breath.
- For a long time, much nauseous, there is vomiting with bile, after which it does not become easier.
- Dry mouth, there is an unpleasant bitterness.
- Sometimes jaundice develops.
- Body temperature jumps to 38 degrees.
If the stone that blocked the bile duct is small, the colic quickly passes. In the case when the disease worsens, an acute form of cholecystitis may occur, in which the gallbladder becomes inflamed. The state is quite dangerous for life. Especially unpleasant is. When it inflammation slowly proceeds, the disease is mild. The patient suffers from pain, unpleasant gravity under the right edge. Also, nausea, severe vomiting. The disease may escalate at any time, so surgery may be prescribed.
How does biliary dyskinesia manifest?
If the motor function of the gall is impaired, it may occasionally disturb. As a rule, discomfort occurs after eating. The patient is constantly suffering from constipation. An attack occurs if a person has eaten something harmful or has experienced extreme stress. Some patients complain of aching, dull pain. But after taking spicy, fatty foods, emotional experiences, the condition worsens dramatically.
Signs of Gallbladder Tumor
If you run gallstone disease, do not treat it, it will end in cancer. In some patients, oncologists accidentally notice a tumor. The patient may complain of discomfort under the right rib, which cannot be arrested with drugs, as well as poor appetite, drastic weight loss. Quite often there is no pain at all, but jaundice appears. And while probing find bumpy, tight seal.
7 main manifestations in diseases of the gallbladder
Pain under the right edge
Have you eaten smoked, spicy, kebabs, drank alcohol and pain? Immediately you can suspect a disrupted body. In addition, discomfort occurs while running, jolly driving, while lifting heavy. There are aching, acute and dull pain.
Important! Pain in the right side of the abdomen is one of the most dangerous symptoms. It is pinpoint, the patient immediately points to the place where the discomfort is localized.
In the case of acute cholecystitis, there is an additional intoxication of the body with a high temperature. But when the tumor pain is constant, it is almost not eliminated with the help of analgesics.
Digestive upset
If there is a problem with bile, the patient loses his appetite, this causes increased flatulence, belching, constipation, or, conversely, diarrhea. All changes occurring in the body are provoked by dyspeptic disorder, in which food ceases to be digested normally.
Raid on the tongue
Due to dyskinesia, tumors and gallstones, the outflow of bile is disrupted, it gets into the mouth, so a yellow color can be seen on the tongue.
Bitter mouth
This is the first symptom of biliary pathologies. Most complain of bitterness in the morning when they wake up. Sometimes it is so strong that the patient refuses to eat.
Yellow skin, mucous membranes
When bile acid is in the blood, jaundice develops. The symptom is most characteristic of the chronic form of cholecystitis.
Calcium discoloration
With the inflection of the gallbladder, different tumors of the feces loses color, becomes white. In this case, the whites of the eyes, the skin is yellow, the patient is bent from pain. This symptom indicates different pathologies, so it is better to pass additional tests.
Dark urine
When bilirubin in the blood rises, the color of the urine changes. What diseases cause this symptom? Again, with dyskinesia, the excesses of the gall, as well as with serious hepatic pathologies.
Diagnostic methods
The doctor first studies the history of the disease, symptoms. After prescribing a biochemical, clinical blood test. It is very important to go through:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- MRI
- X-ray.
- Biopsy.
After the data will be assessed, make a diagnosis. In severe cases, the patient is immediately hospitalized, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If it is not timely to turn to a hepatologist, everything will end in peritonitis, cellulitis, intestinal obstruction, sepsis, cancer.
Thus, all diseases of the biliary system are quite dangerous for humans. It is easier at the early stage to drink choleretic teas, decoctions, infusions, to take, than to get rid of the consequences. Quite often, it is necessary to completely remove the gallbladder, because the organ refuses to function normally. Take care of your health!
