Write a message about medicinal plants. Medicinal plants
Calendar of collecting medicinal plants.
|
Plant name |
Assembled parts |
Collection time |
| Oregano ordinary | Grass | July August |
| Common Oak |
March - May September October |
|
| Hypericum perforatum | Grass | June August |
| Wild strawberry | Fruit | June August |
| Stinging nettle | Leaves | May - September |
| Horse chestnut | May June | |
| Burdock | Root | April - October |
| Dandelion officinalis | The roots | April - October |
| Coltsfoot | Flowers | March - August |
| Chamomile drug | Inflorescences | May - August |
| Celandine big | Grass | May - August |
| Rosehip brown | Fruit | August - October |
| Yarrow | Grass | June August |
| Apple tree forest | Fruit | July August |
St. John's wort - a perennial herbaceous plant of the family of mammals, 30-100 cm tall. The leaves are small, opposite, sessile, oblong-oval, with numerous dotted translucent essential oil glands. The flowers are golden yellow with black stripes, gathered in paniculate inflorescences. It blooms from June to August. It grows throughout Russia, with the exception of the Far North. Hypericum grass is harvested as a medicinal raw material during the flowering period. Applied with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the kidneys, bladder, bedwetting, colds, flu, heart weakness, pulmonary tuberculosis, cancer, headaches, nervous diseases, as well as round worms. Prepare an infusion or decoction of herbs (1 tablespoon to 1 cup of boiling water), drink 1 / 3-1 / 2 cup 3 times a day for 20-30 minutes before meals.

Oregano ordinary - a perennial herbaceous plant of the family Labiatae, 30-60 cm in height and more, with a branched rhizome and numerous tetrahedral and softly steamed stems. Flowers, purple-pink, are collected on the top of the stem in corymbose panicles. It blooms from early July to August. It grows almost throughout Russia. For medicinal purposes, harvest Oregano grass during the flowering period. Apply an infusion of herbs as an expectorant for diseases of the respiratory system, to stimulate appetite and improve digestion (with hypo-and anacid gastritis), liver disease, pulmonary tuberculosis, hypertension, convulsions, epilepsy, neurosis, increased sexual excitability and painful menstruation. Infusion is prepared at the rate of 1:20. Drink 1 / 3-1 / 2 cup 3 times a day for 20-30 minutes before meals. Oregano is contraindicated in pregnancy.

Common Oak - tree of the beech family, reaching 40-50 m in height. WITH therapeutic purpose use the bark of young shoots in early spring during sap flow, before leafing. The bark has anti-inflammatory and astringent action. Used for rinsing, douching, local baths (when sweating feet), washing, lotions (for chronic purulent ulcers, skin diseases). Inside is used for bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, liver and spleen diseases, poisoning by heavy metals, fungi, as well as enteritis, inflammation of the bladder and urinary tract. Oak bark is part of many medicinal fees.

Wild strawberry - a perennial herbaceous plant of the Rosaceae family, 5–20 cm tall, with trifoliate leaves with large-toothed leaves. The flowers of the wild strawberry are white, the fruits are bright red berries. It blooms in May and June, the fruits ripen in June and July. Berries, leaves and less often rhizomes of strawberries are used for the therapeutic purpose. The leaves are collected during the flowering period, rhizomes dug in the fall. A decoction of berries and leaves is taken in case of metabolic disorders (including diabetes mellitus), in the treatment of gout, kidney stones and liver, and bladder diseases. A decoction is prepared from the leaves (2-3 tablespoons of dried, crushed leaves per 500 ml of boiling water) ). Drink 1/2 cup 3 times a day for 20-30 minutes before meals. A decoction of the berries is prepared at the rate of 4 tablespoons of dry berries per 500 ml of boiling water. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day. Fresh strawberries are a good remedy for anemia, atherosclerosis, metabolic disorders, diseases of the spleen. For some people, poorly digested strawberries.

Stinging nettle - A perennial herbaceous plant of the nettle family, all covered with stinging hairs. Flowers inconspicuous, light green. It blooms from mid-June to late autumn. For therapeutic purposes in July and August, the leaves are collected from flowering plants. Roots are also harvested with rhizomes. It is widespread as a weed plant. Applied with bleeding, diabetes, anemia, bronchitis, bronchial asthma, tuberculosis, whooping cough, bowel disorders, dysentery, splenic diseases, liver, kidneys, rheumatic disease, obesity, gout, atherosclerosis, abrasions, eczema, shingles, irregular menstruation, nerve seizures, cancer diseases. Outside, the juice, infusion or decoction of nettle is used in the treatment of wounds, burns, difficult healing ulcers, tumors, and also to stimulate hair growth. Infusion, decoction (2 tablespoons of nettle for 500 ml of boiling water) drink 1 / 5-1 / 4 cup 3 times a day for 20-30 minutes before meals. Juice dosage: 20-30 drops per 1/4 cup warm water 20-30 minutes before meals 3 times a day.

Burdock - biennial large-grass plant of the Compositae family, up to 1.5-1.8 m high, with a thick taproot, large petioles up to 50 cm in length and approximately the same width. Widespread in Russia. The roots and leaves of the plant are used. The leaves are harvested in June-September, the roots - in the fall in the first year of growth. Applied with gout, rheumatism, pulmonary tuberculosis, diabetes, gastric ulcer, gastritis, stones in the kidneys and liver, hemorrhoids, chronic constipation of skin diseases, ulcers, to strengthen the hair, as well as an antitumor agent. Fresh burdock leaves are washed and applied in 5-6 layers to the sore spot with radiculitis and joint pain. Such a treatment is also effective with heel spurs. From the roots they prepare a decoction (1:20) and drink 1/2 cup 2-3 times a day.

Dandelion officinalis - perennial herbaceous plant of the Compositae family, with a fleshy root. Mass flowering is observed in May. Medicinal use are mainly the roots of the plant, at least - the leaves. The roots are harvested in the fall, during the period of leaf withering. Dandelion preparations are used for skin rashes, acne, boils, coughs, to stimulate the excretion of milk in nursing mothers, as an antipyretic, diaphoretic, tonic and blood purifying agent, and also as a means of promoting the dissolution of gallstones and has a calming effect on stones, sand in the kidneys and bladder and their other diseases. Infusion and decoction of dandelions are also useful in diabetes, digestive disorders, tuberculosis and cancer. An infusion or decoction is prepared at the rate of 1 tablespoon of dried, shredded roots per 1 cup of boiling water. Drink in the form of heat 1/3 cup 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Infusion and decoction of the leaves (2-3 tablespoons of dry crushed leaves per 500 ml of boiling water), drink 1/2 cup for 15-20 minutes before eating. Young leaves are useful to include in salads.


Fragrant daisy . Drug chamomile is not easy to find, and often, instead, it harvests the yellow heads of a crackless, strongly smelling chamomile, which is abundant everywhere. This daisy is tongueless or fragrant (fragrant). She loves settling in the courtyards, the streets and squares of provincial towns, cover football fields, airfields. She, like the plantain, is resistant to trampling. Chamomile odorous - a small plant, usually not exceeding 5-10cm. She comes from America. In the 1840s, it could be found only in the St. Petersburg Botanical Garden. However, since the 1870s of the last century, it has only spread throughout Russia within 30–40 years. How did this so swift, wonderful settlement take place? It turns out that chamomile is fragrant as a weed growing in the fields, got into the grain supplied from America, and with it - to the fields. Being medicinal, it began to be used as a substitute for camomile pharmaceutical. Chamomile odorous is used more often outwardly (as a substitute for chamomile pharmacy). Inside it is drunk by the people in the form of infusions and decoctions prepared at the rate of 3 tbsp. spoons of dry crushed flowers to 0.5 liters of water. Chamomile infusions and decoctions are recommended for bowel spasms, worms, gastritis, diarrhea, spastic colitis, allergies, kidney disease, and also as an anticonvulsant and sedative for epilepsy. The plant may be part of antitumor fees.
pharmaceutical camomile - herbaceous annual plant of the Asteraceae family, 20–40 cm tall, with erect stem and pinworm leaves. At the ends of the branches of chamomile are baskets of yellow flowers, bordered with white petals. The camomile pharmaceutical in June-July blossoms. It grows everywhere in all regions of the European part of Russia. Chamomile inflorescences are harvested at a time when reed flowers have only assumed a horizontal position (remnants of the flowering stem should be no more than 3 cm). It is used for diarrhea, flatulence, intestinal spasms, acute and chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, enterocolitis, liver and bile duct diseases, kidneys, colds, allergies and cancer, painful menstruation. Outwardly, they are used for rinsing, lotions, baths, enemas and douches for stomatitis, tonsillitis, sore throat, toothache, diseases of the female genitalia, hemorrhoids, skin diseases, and also to strengthen the hair. Infusions and decoctions (3 tablespoons of dry crushed flowers per 500 ml of boiling water) drink 1/2 cup 3-4 times a day.
Greater celandine (Greater celandine) - perennial herbaceous plant of the poppy family, 30-90 cm high. The stem is branched, densely leafy. The leaves are large, pinnately dissected into rounded lobes, bright green above, glaucous below. The flowers are golden yellow, on long stalks, 3-8 clusters are collected in the inflorescence - a simple umbrella. It blooms in May and July. The plant is poisonous. Harvest mainly celandine grass (harvested at the beginning of flowering), less often roots (dug out in the fall). The complex of biologically active substances, primarily alkaloids, provides a wide range of pharmacological activity of the herb celandine. The main types of action include anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, choleretic and some analgesic effect. Fresh juice of celandine has a virusostatic effect. The antispasmodic activity of the herb of the celandine is due to the action of the main alkaloid chelidonin, and chelidonin also has a calming effect on the central nervous system (morphine-like action). Homochelidonin, in contrast, has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, can cause convulsions, has local anesthetic activity. Alkaloid protopin reduces the reactivity of the autonomic nervous system and, unlike chelidonin, increases the tone of smooth muscles. The amount of alkaloids sanguinarine and cheleretrin (sanguinarine) has a distinct anticholinesterase effect. Sanguirythrin bactericidal effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as yeast-like fungi and trichomonads. Indications for external use are poorly healing wounds, skin tuberculosis, eczema, warts, corns, herpes; for oral administration - diseases of the liver, gallbladder, gout. The prepared infusion (5 g of raw material per 200 ml of water) is ingested 1 / 2-1 / 3 cups 2-3 times a day. Outwardly - in the form of infusion or fresh juice. When ingestion, nausea and vomiting are possible, when applied externally, local skin irritation. Contraindications for oral administration - epilepsy, bronchial asthma, angina. If ingested in case of overdose, paralysis of the respiratory center is possible. Not recommended for use during pregnancy. Can be used as part of monotherapy and combination therapy.
Rosehip Cinnamon (Rosae) - shrub of the Rosaceae family, 1-2 m high, with firm, curved and rarely located spines. Leaves are pinnate, 4–9 cm long, with 5–7 leaflets and herbaceous stipules. Flowers pink with a diameter of 3-5 cm, often single, at least 2-3 together. It blooms from mid-May to July. The fruits ripen in August and the first half of September. Rose hips are very rich in vitamins (especially vitamin C) and mineral salts, they are harvested for medical purposes. Apply dogrose broth for gastritis (especially with low acidity), catarrhal diseases, anemia, various bleeding, to improve digestion, for gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, as well as for atherosclerosis, neurasthenia, lung, kidney, bladder, gout, disorders metabolism, depletion of the body, fractures, wounds, diseases of the liver and biliary tract, tumors, intoxication, exposure to adverse environmental factors. The pharmacological activity of rose hips is determined mainly by a complex of vitamins (vitamins of group B, vitamin E, vitamin P, carotene) and, first of all, ascorbic acid. Stimulates nonspecific resistance of the body, enhances tissue regeneration and hormone synthesis, reduces vascular permeability, takes part in carbohydrate metabolism, has anti-inflammatory properties. Rose hips are used for the prevention and treatment of hypovitaminosis C and P. Prepared infusion (10 g of raw material per 200 ml of water) is taken orally for 1 / 4-1 / 2 cup twice a day; children - 1 / 8-1 / 4 cup at the reception. Cooked infusion stored in a cool place for no more than two days.

Yarrow - perennial herbaceous plant of the compositae family, height 20-100 cm, with finely dissected leaves. The flowers are white, rarely pink, collected in baskets. It blooms from July to September. It grows in forest and forest-steppe zones in dry meadows, along the edges of fields in the European part of Russia. For the purpose of treatment, the yarrow herb is used, which is harvested during the flowering period, cutting off the upper part of the stem (about 15 cm long). Assign yarrow bleedings, gastritis, gastric ulcer, colitis, and enterocolitis, flatulence, diabetes, cholecystitis, lack of appetite, sluggish digestion, varicosity, inflammation of the urinary tract, bedwetting, gynecological diseases, benign and malignant tumors, tuberculosis, gout, rheumatism. An herb is used to make an infusion or decoction (2 tablespoons of dry finely chopped herb per 500 ml of boiling water) and drink 1 / 3-1 / 2 cup 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. External decoction is used to treat wounds, ulcers, diathesis, scabies, scaly depriving, eczema, as well as for rinsing and douching.
Apple tree forest - The fruit tree of the rose family. Many varieties of apple trees are cultivated in our country. Along with its fruits are used and the fruits of wild apple. They contain malic, tartaric, citric and other organic acids, sugars (glucose, sucrose), vitamins C, A, B1, carotene, tannins, trace elements (iron, potassium, calcium, magnesium), essential oil. Apples are rich in iron, in connection with which they are used for the manufacture of a pharmacological drug - malic acid iron, used in the treatment of anemia (anemia). AT traditional medicine Apple gruel is used as a healing agent for abrasions and other skin lesions, as well as for nipple cracks in nursing mothers. Fresh fruits are used in hypo-and avitaminosis, in inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines (as a means of improving digestion and normalizing metabolism), and also as a fortifying agent. Apple tea is drunk for urolithiasis, gout, rheumatism, gastrointestinal and other diseases. Tea from the leaves and flowers of the apple helps with colds. Apples are pretty well kept. So, fresh fruits, laid out in a single layer, in unheated rooms can last up to 3-5 months. Dried apples (dried at 70 ° C) is a good source of easily digestible sugars, as well as trace elements, but they lose a significant amount of vitamins and aromatic substances. In pickled apples, vitamins are better preserved, but their consumption should be limited to those who have liver, stomach and kidneys. For people suffering from gastrointestinal diseases, apples are especially useful because they contain tannins with astringent effects, and apple pectin substances adsorb and excrete various toxic compounds from the body. Therefore, for example, in dysentery and colitis, raw and baked grated apples are prescribed, in which there are especially many pectins. In addition, apples are a source of vitamins, however, their content is relatively small with the exception of vitamin R. One or two apples can provide the daily human need for this vitamin and for trace elements absolutely necessary for the body. Apples are especially useful for those who have oxalate stones in the kidneys (formed in connection with the disturbance of calcium and oxalic acid metabolism), as they have the properties to remove oxalates from the body. It should be noted that apples are widely used in therapeutic diets. So, sweet varieties of apples are used in diseases of the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system, and sour - in diabetes and obesity. Very beneficial effect on health and health unloading apple days. In recent years, in special studies conducted in France, America, Italy and other countries, it has been shown that eating apples decreases the absorption of fats by the body, which contributes to the elimination of excess cholesterol. Among those who regularly eat apples, more than half have cholesterol levels 10% lower than those who do not eat apples. Even if you eat only 2-3 apples daily, you can significantly reduce the level of cholesterol in the blood. Such a therapeutic effect of apples is explained not only by the presence of a large amount of pectic substances in them, but also by the presence of vitamin C of trace elements and other substances that enhance the actions of each other. It is also interesting that taking apples can reduce not only the amount of various fatty acids circulating in the body, but also make their ratio more favorable. Thus, it is clear that if a person consumes a lot of fatty foods and sugar, then the inclusion of apples in the diet, and especially holding fasting apple days, will prevent the body from absorbing excess fat.
Plant ivan da maria
(Melampyrum nemorosum L.), otherwise called by the people: maryannik dubravny, brother and sister, bro, medunka, zheltyanitsa, diarrhea, fireflower, jaundice, Ivanova grass, tricolor grass, meadow bell - one of the four flowers of the attributes of a fortune wreath for Ivan's holiday Kupala. But more and more he is known as the plant Adam-and-Eva (Ivan-da-Marya)) ...
The people believed that the flowers of Ivana da Marya, collected on Kupala protect the house from black people all year, and the grass restores peace in the family between the spouses. The plant is also interesting because its seeds attract the ants with their fragrant sack, as a result they take them around the forest, spreading the herbaceous plant, an annual plant of the family of wormwoods, ivan da Marya, grows 15–50 cm in height. suckers, which are attached to the roots of other plants and fed from them juice. The stem of marianica dubravnogo - branched, straight, pubescent with whitish hairs down. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate, opposite, whole-extreme, long-pointed. The flower of Ivan-da-Marya is drooping, all the flowers are sitting one by one on short pedicels, in the axils of the upper leaves, turned in one direction, grouped into a loose brush. Each flower has a bract leaves, purple, bright purple, crimson or blue, more intense color at the top. The corolla is bright yellow, the long-cap calyx. The fruit of Ivan da Marie is a box in the shape of an egg, opening up divided into two. Flowering plants can be observed from the end of spring until autumn. The plant contains glycoside dulcite, alkaloids, poisonous glycoside aukubin is found in the seeds. Traditional medicine has been used infusion of herbs in diseases of the heart, stomach, urticaria, scrofula, and externally used in the form of washing and baths for various rashes, scrofula, scabies and eczema, diathesis and tuberculosis of the skin. Fresh crushed aboveground part of the medicinal plant heals wounds. Water decoction of the fruits of the plant Ivana da Marya is used to kill insects as an insecticide. Also, the herb Marianica Dubravnogo used for epilepsy. The legend of the flower, Ivan-da-maria, speaks of the young man, Ivan, and the girl, Marya, who have decided to never part and turn into beautiful flowers. Since then Ivan has a purple shirt, and Mary has a yellow kerchief. So they stand nowhere without each other ... In memory of two loving hearts, the people called Ivan-da-Marya.
Plantain - This is a plant from the Podorozhnikov family, of which there are about 200 species in total, and they are distributed all over the globe, but many of them are weeds. Among the medicinal plants there are several types of plantain: large and flea - both of them are very valuable. They can be found near the roads (hence the name), in the wilderness, in the steppe places, in the meadows, and even sands. The plant is also an excellent nutritional food for many types of butterflies.
Healing properties
The hero of our message, and this is known, has anti-inflammatory, hemostatic effect, promotes healing of wounds. Only the leaves of this plant must be chewed or crushed to highlight the juice. Apply them to wounds for disinfection and speedy healing.
Plantain's toothed leaves in some European countries are used as a vegetable plant, and when it is grown in vegetable gardens, various vitamin salads are made from it.
The Legend of Plantain
There is a legend that tells about how they discovered the healing properties of plantain. Two snakes cozily settled down on the road and basked in the sun. Suddenly, a cart appeared from around the corner. One snake managed to crawl away quickly, and the second lingered, and the wagon crushed it. The people who were sitting there saw the first snake crawl away, but later returned with a plantain leaf, with which it healed the second snake.
Story
Plantain ordinary is considered one of the medicinal plants. Even in ancient China, engaged in its collection for medical purposes. In ancient Greece and Rome, inflammation of the stomach, dysentery and other diseases used its seeds. It was used by Hippocrates and Galen. According to Avicenna, plantain is very good for ulcers. Its leaves have an astringent property. They stop bleeding, and in the dried state help to heal old and fresh ulcers.
Infusion of the leaves of the plant is used for medical purposes: for example, as an expectorant, digestive agent.
Use of psyllium
Young leaves are used for soups, light salads. They are used for making vinaigrettes, side dishes for meat and fish dishes. Seeds that ferment in milk can be used as a seasoning. In folk veterinary medicine, dry leaf powder is used to treat anthrax. Plantain is an excellent honey plant. It is very useful and easy to find and use.
If this message came in handy for you, she is glad to see you.
Younger students about medicinal plants
Conversation "Medicinal plants" for younger students. Material from a photo
Noskova Natalia YurievnaPosition and place of work: primary school teacher MBOU - Verkh-Tulinskaya Secondary School № 14 Novosibirsk region
Description: I present to your attention the material on medicinal plants, annually harvested in significant quantities for the medical and other industries. This work may be of interest to teachers, kindergarten teachers and students.
Purpose: The material is intended to replenish the piggy bank of teachers.
Purpose: familiarization with medicinal plants.
Tasks: - expand and deepen children's knowledge about medicinal plants;
- develop interest and desire to learn more about plants;
- foster respect for plants and love for nature.
Rational use of resources
On the territory of our country grows a lot of plants that are of great value for medicine and various industries. Consumer cooperation organizations annually procure over 80 species of such plants. The demand for them is constantly growing.
In this regard, it is important in the organization and conduct of preparations of medicinal plant materials to protect the existing thickets from depletion, which occurs during unlimited use of sites. Plants that are in high demand, slowly multiply or harvested before the end of the growing season are exposed to such danger. For example, when gathering linden flowers it is impossible to break off large branches, as this leads to a sharp decrease in tree productivity. Harvesting the bark from the main stem of viburnum, buckthorn leads to drying of the tree or shrub. Plants are also at great risk when their roots and rhizomes are harvested (marshmallows, aralia, elecampus, nipponian dioscorea and others).
In order to ensure the full restoration of the thickets and the use of plots for many years, it is necessary to alternate each year the areas of gathering raw materials and leave developed plants on each of them. Practice shows that this is the most common way of keeping blanks.
I present you several types of medicinal plants.
Althaea officinalis
Alley - a perennial, grayish-green herbaceous plant, reaching up to 1.5 m in height with pinkish flowers. It grows along the banks of rivers and lakes, on meadows, in bushes. It is found in the southern strip of the European part of our country, in the Caucasus and in the south of Western Siberia.

Althea roots dig up in the spring and autumn. In order to preserve thickets, it is necessary to produce billets in the same area no more than once every 3-4 years and leave up to 30% of young plants. The aboveground part of the plant and the main taproot are cut and removed. Side roots, carefully peeled from the ground, are dried, removing the upper cortex (peel) from them with a sharp knife. Thick roots are cut lengthwise, long across, into pieces up to 35 cm, and then dried in the open air, in ovens or dryers at a temperature not exceeding 40 degrees, since at higher temperatures they turn yellow.

The roots are rich in mucous substances, starch, sucrose. Infusion of the roots made on cold water, has enveloping, expectorant and anti-inflammatory properties.

It is used in catarrh, bronchitis, inflammation of the lungs, gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract.

Immortelle sandy (or Cmin sandy) is a perennial plant with a height of 15-30 cm with spherical lemon-yellow flower baskets. It is widely distributed in the steppe regions of the European part of our country, in the North Caucasus and in Southern Siberia.
Collect not fully bloomed inflorescences-baskets (June-August). The inflorescences are cut off with the rest of the stem not longer than 1-2 cm. On the same immortelle array, the collection of inflorescences can be carried out up to 3-4 times as the plants bloom. Re-collection is usually carried out in 5-7 days.
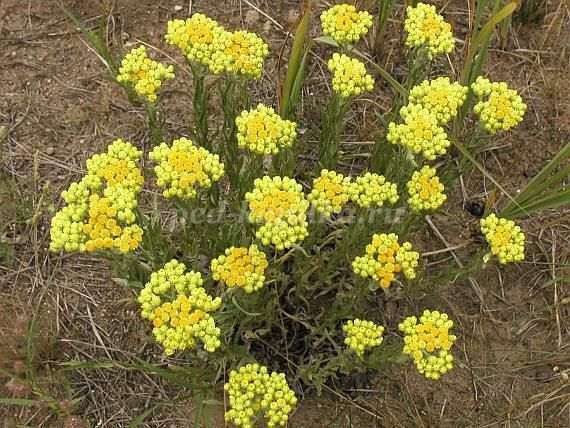

You can not tear the inflorescences with stems, and even more to pull out plants with roots - this leads to the destruction of thickets. The immortelle can be collected on the same array for several years in a row, provided it remains on 1 square meter. m thickets of 1-2 flowering plants to ensure seed renewal.

Dry in a dark, well-ventilated area. Flowers retain a lemon-yellow color and after drying.

Immortelle sand has a therapeutic effect in diseases of the liver, gallbladder and gastric pathways; stimulates the function of the stomach and pancreas, improves metabolism.
Immortelle preparations prescribed for gastritis, pancreatitis.
Immortelle preparations can not be taken more than 3 months in a row. This group of drugs increases blood pressure, with hypertension, long-term use is contraindicated.
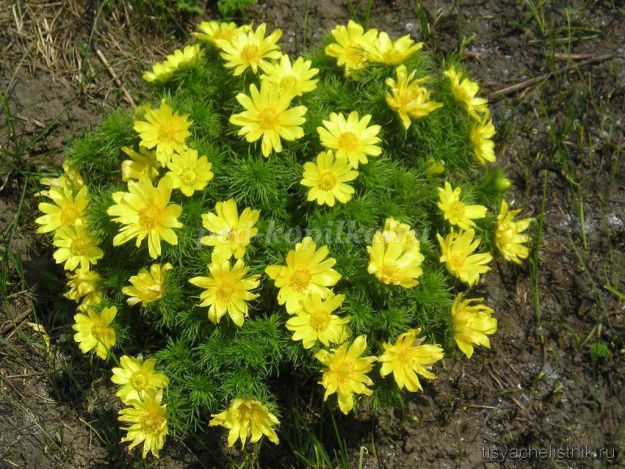

Adonis - a perennial herb up to 40 cm tall with large bright yellow flowers. Blossoms in April-May simultaneously with the appearance of leaves. Occurs in mixed grass and grass steppes, in glades and along the edges. It is distributed in the middle and southern strip of the European part of our country, in the North Caucasus, in the steppe part of Siberia to Krasnoyarsk.

Gather grass in the flowering period before the fruits fall. Acrobate is harvested by cutting the plant with a sickle, shears, scissors or mowing along with grass. Cut the adonis above the brown scales, at a height of 5-10 cm from the soil surface.

You can not pull out the plant with the root, as this leads to the destruction of the undergrowth, recovering very slowly. When harvesting part of the bushes (per 100 sq. M - 1-2 good bushes) should be left uncut for planting.
Dry the grass immediately after picking in the open air in the shade, or in dryers at a temperature of 50-60 degrees.
Adonis is widely distributed in folk medicine. It contains the following substances: anitoxin, saponins and tsimarin. Adonis normalizes heart function, and this plant is very often used as a diuretic.
Adonis is used when coughing, colic, colds and dropsy. It is used as a sedative for convulsions, fever and pain in the head.

With the help of Adonis, you can get rid of shortness of breath, swelling.

Adonis is considered a panacea for all diseases. That is why it is very difficult to find, and some cannot see this plant at all.

Do not forget that adonis is a poisonous plant!
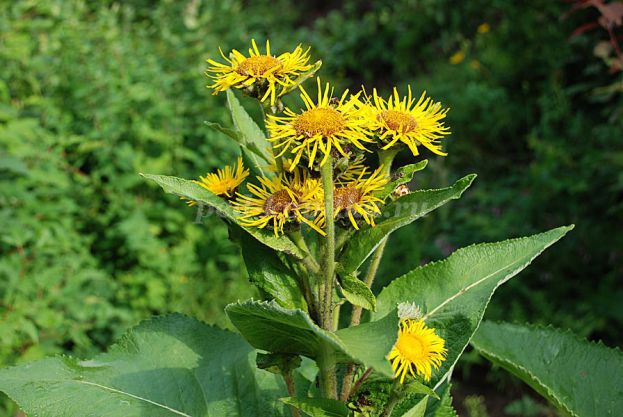

Devyasil is a perennial wild-growing herbaceous plant up to 1-2 m high. It grows on wet places, floodplains of rivers, on forest glades and edges, among thickets of bushes, on clearings, in sparse deciduous forests. Distributed in the Volga region, in the Caucasus, Altai.

Rhizomes and roots devyala dig in the fall or early spring. The plant cuts off the aerial part, undermines the root system to a depth of 30-35 cm in a radius of about 35 cm around the stem, pruning the rod and lateral roots. The formed hole is covered with soil to ensure the growth of the remaining roots. To save the thickets for about every 10 square meters. m. leave at least one adult plant. Young, non-flowering plants should not be dug out.
![]()
Dug roots are thoroughly cleaned from the ground, quickly washed in cold water, cut into pieces and dried in the open air, in ventilated rooms or dryers at a temperature of 50-65 degrees.
Plantago major L. Plantain family - Plantaginaceae
Plantain - An old medicinal plant. He was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans, he was highly appreciated by Arab and Persian doctors. The Latin name of the plantain is formed from the "plant" (sole) and "Ager" (move), since its leaves resemble a footprint. The Indians of America noticed that he accompanied the appearance of the Europeans, and called him "the trace of the white man." The Russian name of the plant indicates the place of its growth.
This is a perennial herbaceous plant 10-40 cm tall with one or more floral arrows "and a rosette of basal long-petiolate, entire, broadly ovate, naked green leaves with pronounced longitudinal veins. Floral arrowheads end in a long cylindrical spike of small brownish flowers up to 30 cm tall. The fruit is a two-fold drop-down box that blooms from May to September.
It grows in wastelands and weedy places, near housing, near roads, on green meadows, fields, vegetable gardens, gardens, forest edges and banks of reservoirs. Distributed throughout the CIS, except for the Far North. It grows everywhere in the south of Russia.
Another type of plantain is also used - the plantain is blach, characterized by smaller lance-linear leaves. In medicine, use plantain leaves large. They are harvested during the period of full bloom, carefully tearing off fully developed green intact leaves with a stem of no more than 5 cm. Drying is carried out immediately, immediately after collection, in ventilated and protected from sunlight rooms, spreading the leaves in a very thin layer, turning over periodically. Brown and yellowed leaves are removed. Dried raw material consists of a green, odorless, whole, bitterish, slightly astringent taste.
Plantain leaves contain mucus (up to 10%), aukubin glycoside, carotene, ascorbic and citric acid, vitamin K, bitter and tannins, potassium, resins, saponins, sterols, enzymes. Fresh leaves of the plantain and preparations prepared from them have a hemostatic, bactericidal, wound healing, hypotensive and expectorant action. Juice of fresh plants and water infusion of leaves is especially effective in the treatment of gastric ulcer and intestinal ulcers, dysentery and dyspepsia, colitis, enterocolitis, diseases of the bladder, upper respiratory tract, bronchi and lungs. The infusion of leaves helps to dilute and dissolve sputum and is one of the best expectorant for bronchitis and pulmonary tuberculosis.
In folk medicine in many countries, fresh plantain leaves are used as a wound-healing and anti-inflammatory agent for wounds, ulcers, insect bites, bees, and vipers, as an analgesic and tumor-preventing agent. In scientific medicine, dried leaves of plantain is used as an infusion as an expectorant.
Infusion is prepared according to the general rules at the rate of 2 tablespoons of finely chopped leaves into a glass of water. Take 1 / 2-1 / 3 cup 3-4 times a day 15 minutes before meals. The industry produces leaves in the form of briquettes, plantain juice, which is a mixture of juice from freshly harvested leaves of large plantain and plantain fleas; plantaglyutsid in granules - the total drug from the water extract of the large plantain; plantain tincture. Plantain leaves are part of the collection of the chest number 2.
